Thematic Analysis in Qualitative Research: Manual vs ChatGPT?

Thematic analysis, done either by AI or a human, is one of the most widely used methods of interpreting qualitative data, such as interviews, field notes, and social media posts. There is no doubt that with the right prompt, a free AI tool such as ChatGPT can analyze text data with less bias than a human being.
Manual coding is easy to learn and effective on small data sets, but what about when the data becomes large and complex? Would a more advanced AI tool be effective?
At a Glance
What is Thematic Analysis in Qualitative Research?
Simply put, thematic analysis refers to the process of identifying and analyzing themes within qualitative data. Allowing, for instance, the frequency of themes to be plotted and interpreted so that researchers may understand underlying meanings and the experiences of participants.
This technique is particularly useful for exploring complex data sets where the goal is not just to count occurrences of specific words, but to understand the broader context and significance of what surveyed individuals are expressing.
Let’s break thematic analysis down into a dual approach.
Inductive Approach: The researcher takes codes and themes that emerge directly from within the data itself, developing an analysis based on what they find.
Deductive Approach: The researcher applies a pre-existing framework or theory to guide the coding process
Ready to find themes in your text?
Start a free trial of Displayr.
Start a free trial
Manual Method of Thematic Analysis
The original manual method of thematic analysis originated from psychologists Braun and Clarke in 2006, and is - while time-consuming - widely understood to be effective. There are 6 phases.
Phase 1: Familiarizing Yourself with the Data
Read and re-read through your text data, getting a sense of context and noting patterns that occur. Try to be as unbiased as possible, putting aside any preconceptions about what you expect to read.
Phase 2: Generating Initial Codes
Once you're familiar with the data, the next step is to start coding. This involves documenting patterns inductively or deductively by grouping them together with phrases.

Here’s an example of the coding process.
Phase 3: Searching for Themes
After coding the data, you begin to group related codes into themes. A theme is a broader, overarching concept that links together several codes under a common idea. This can be a tedious step to do manually, but it’s crucial to spend time more deeply considering the connections between codes to ensure your themes accurately reflect your qualitative data.
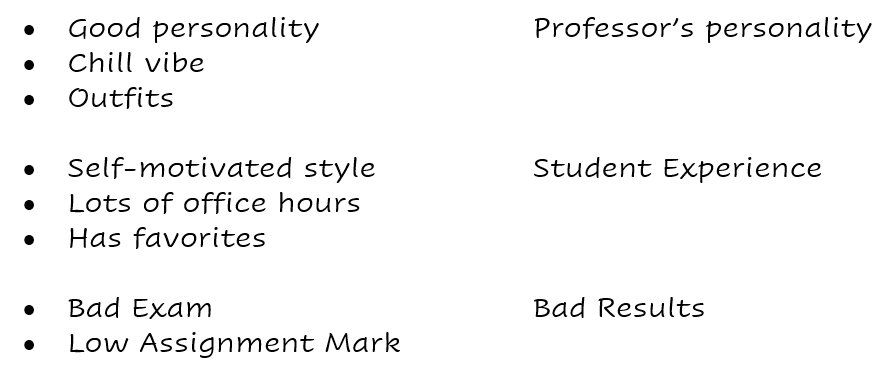
Grouping the previous codes into comprehensive themes.
Phase 4: Reviewing and Refining Themes
Once you've identified potential themes, review them and consider if they support the data and general perspective. If not, revisit the data and merge themes or break larger ones up.
Think about connections and relationships between your themes – should two themes be merged? Or should they be separate themes where their similarity provides valuable insight?
For instance, the researcher in our example could decide to narrow down the ‘Student Experience’ theme for a more precise focus on different experiences.
Phase 5: Defining the Themes
Clearly define and name each theme so they accurately represent the data and portray what you mean as the researcher. Contextualize each of your themes, considering if they truly contribute towards answering your research question.
Let’s return to our example. Maybe the researcher didn’t previously narrow it down and instead concludes that the data currently under “Student Experience” would better answer their research question if the theme were renamed “Professor’s Teaching Style”.
Phase 6: Writing Your Report
Now it’s time to write up your report. You should be offering an overview of the codes and themes. Analyze your data and answer your research question with the results from your thematic analysis of qualitative data.
ChatGPT For Thematic Analysis
One of the main challenges in manual thematic analysis is innate human bias. A free AI tool such as ChatGPT can, with the right prompt engineering, code and theme your text data for you.
Let's take our previous survey response example, and see how ChatGPT compares to the manual method in phases 2 and 3.

First ChatGPT coded the survey response - these codes similar to those found with the manual method.
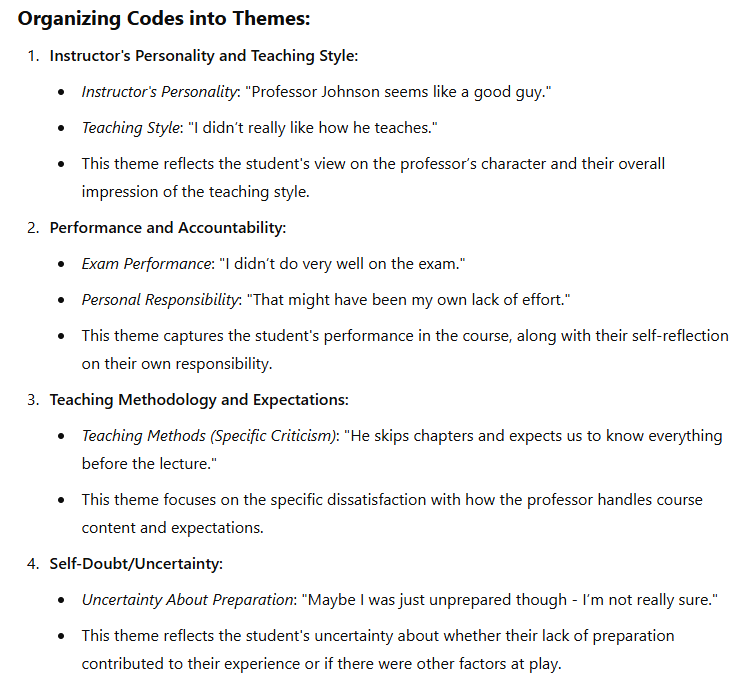
Then, it effectively organized this simple qualitative data into themes.
As you can see, ChatGPT was able to code the text using themes similar to those used in the manual method. There was some discrepancy in the themes selected; however, this is to be expected.
This was an extremely fast and effective way to thematically analyze a small amount of text. However, if we were to move into a larger sample size, we'd start to see ChatGPT's constraints around character limit. Even if you upgrade to the paid version of ChatGPT (GPT-4), you will discover that while more comprehensive than the free version, AI does not have a human EQ.
Not to mention, with longer databases you will still be hit with a character limit.
However, if you think ChatGPT will work for you, you can read our step-to-step guide with prompt ideas on how to use ChatGPT to analyze qualitative data. We’ll run you through how to best use AI to code and theme your text data, boosting you ahead with your thematic analysis.
A More Advanced AI Option for Thematic Analysis
ChatGPT has its pros, but you may be looking to use thematic analysis on a large qualitative dataset or want to perform more advanced analysis. Displayr’s text analytics software requires no coding experience, using AI to classify your qualitative data into themes with just a few clicks.
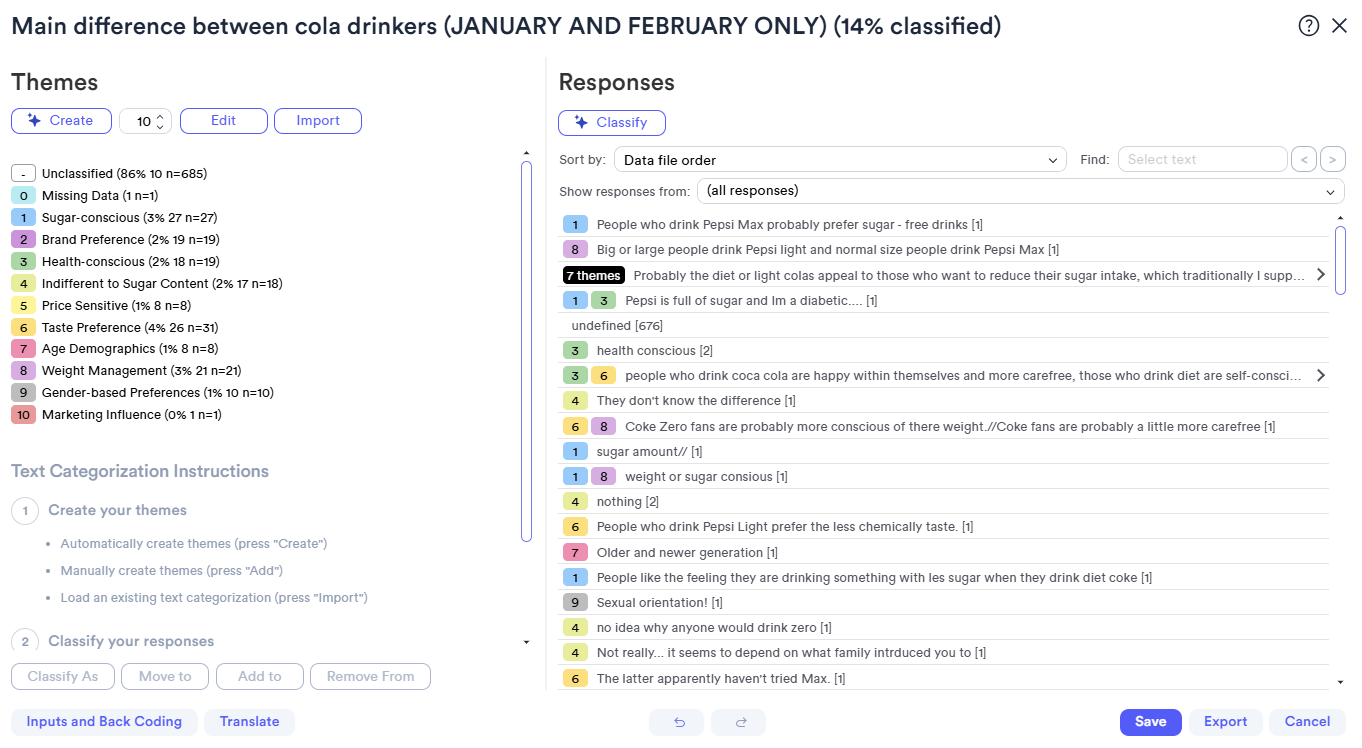
Displayr's AI text categorization will accessibly color code your themes with user-friendly software.
Displayr uses more advanced AI and Natural Language Processing to look beyond the keywords of your text and into it's context and subtext. Moreover, once you've coded and themed your qualitative data using Displayr, you can easily visualize it with crosstabs, dashboards, PowerPoints and much, much more.
As you’ve just discovered by comparing manual and ChatGPT-assisted thematic analysis, there is a trade-off between speed and accuracy.
Learn how Displayr's user-friendly text classification tool can help you achieve a happy medium.